Documents and Links
How to Measure Your Tree
The first step in measuring your tree is to find the single main trunk of the tree. This is typically the largest trunk of the tree.
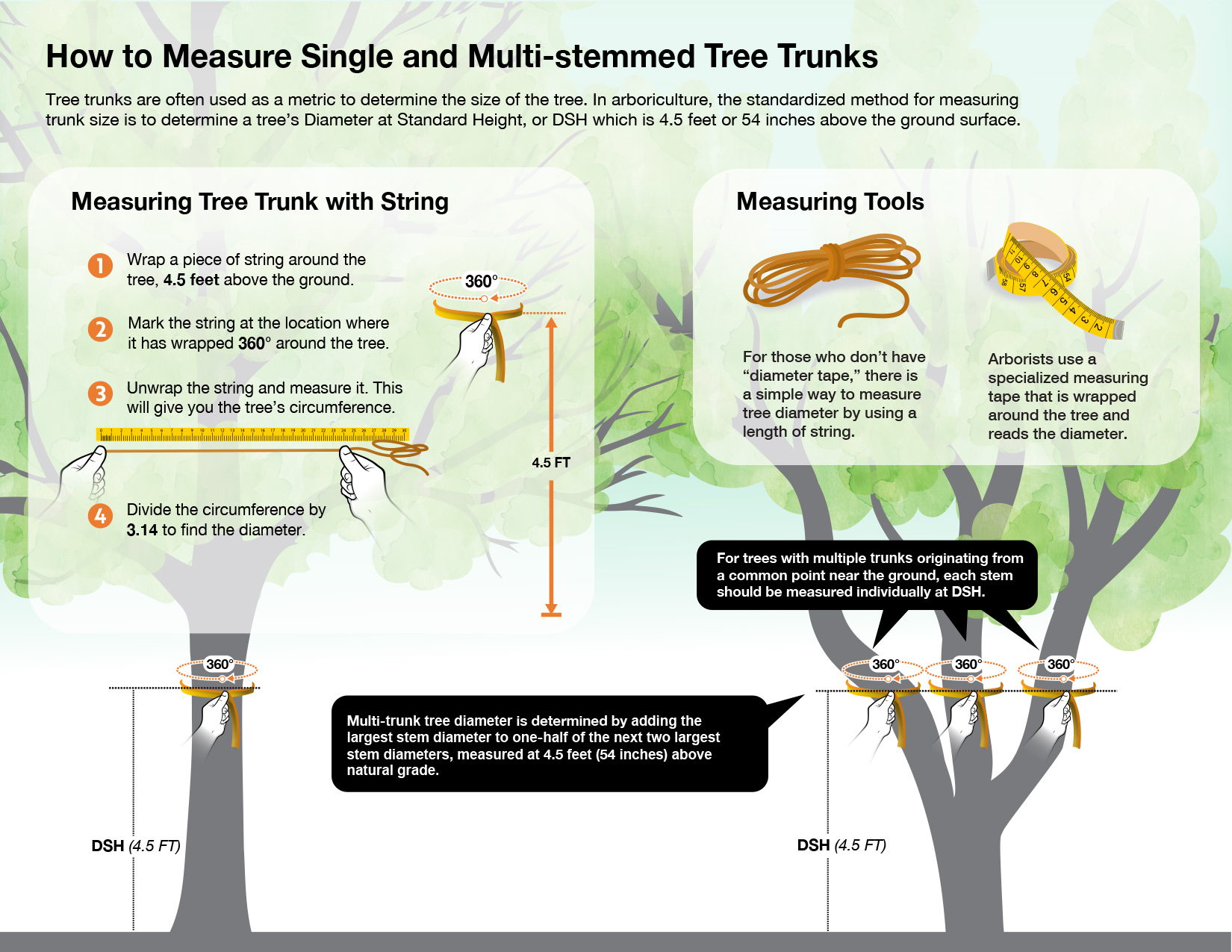
Measuring Tree Diameter: The size of a tree in the arboriculture and forestry industries are often calculated as a standard measuring unit “Diameter at Standard Height” (DSH). DSH is measured at a height of 4.5 feet (54 inches) above natural grade. This measure is commonly done by an arborist during a tree inventory or health inspection using a calibrated tree diameter tape measure. A resident of the County who does not have access to a calibrated tree diameter tape measure may follow the following procedure.
How to calculate tree diameter without a tree diameter measuring tape.
- Measure the tree vertically from ground level to a height of 4.5 feet (54”) above natural grade using standard measuring ruler, tailor’s tape or flexible steel measuring tape.
- At 4.5 feet (54”) wrap the measuring apparatus around the tree to obtain complete circumference. Record result.
- If a flexible tape measure is too short, or you only have a rigid ruler, use a string or rope to wrap the circumference of the tree at 54”. Use a pen or piece of tape to demark where circumference was completed.
- Lay out the string or rope on the ground and use the rigid ruler to measure length from the end of the rope to the marked end point of circumference. Record length.
- Divide recorded length of tree circumference at 4.5 feet (54”) above natural grade by 3.14 to calculate diameter.
Determining Your Tree Species
There are several ways to determine tree species. Most people start by examining the leaves, flowers, seeds, and bark. For some trees, such as California Bay Laurel (Umbellularia californica), or Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus spp.), the strong smell released from a crushed leaf can help with identification. Identifying plants may be challenging at first, but luckily there are plenty of apps and online to help. Plant identification skills are all about pattern recognition, so the skill will develop automatically over time as you begin to pay closer attention to the differences between species.
Web and App based resources:
Books:
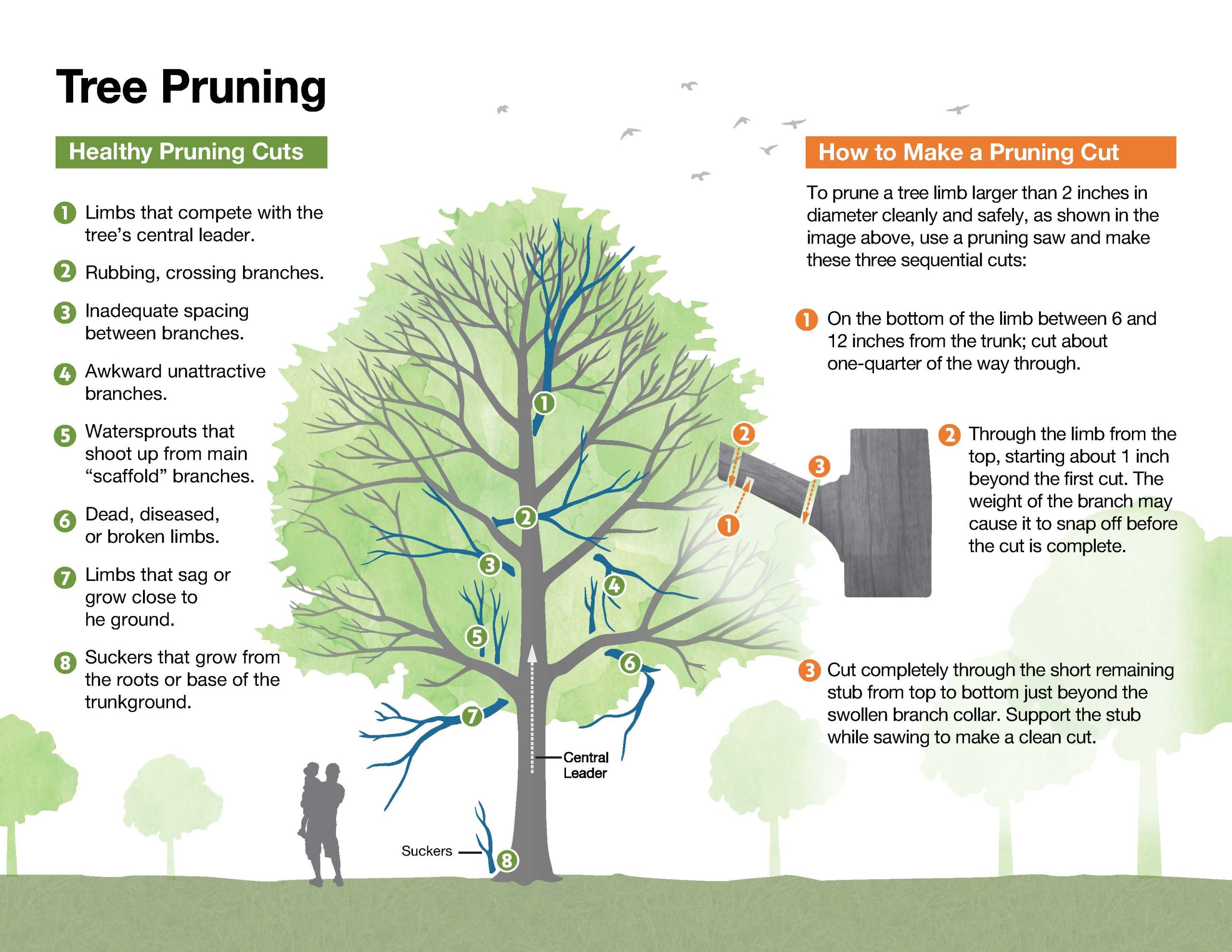
Tree Pruning Guidelines
Proper tree trimming is essential for maintaining the health and structure of trees, ensuring they grow strong and resilient. Removing dead or diseased branches helps prevent the spread of decay and reduces the risk of falling limbs, which can pose safety hazards. The accompanying image will provide everything you need to know in order to perform healthy pruning cuts, including which branches you should prioritize with your trimming.
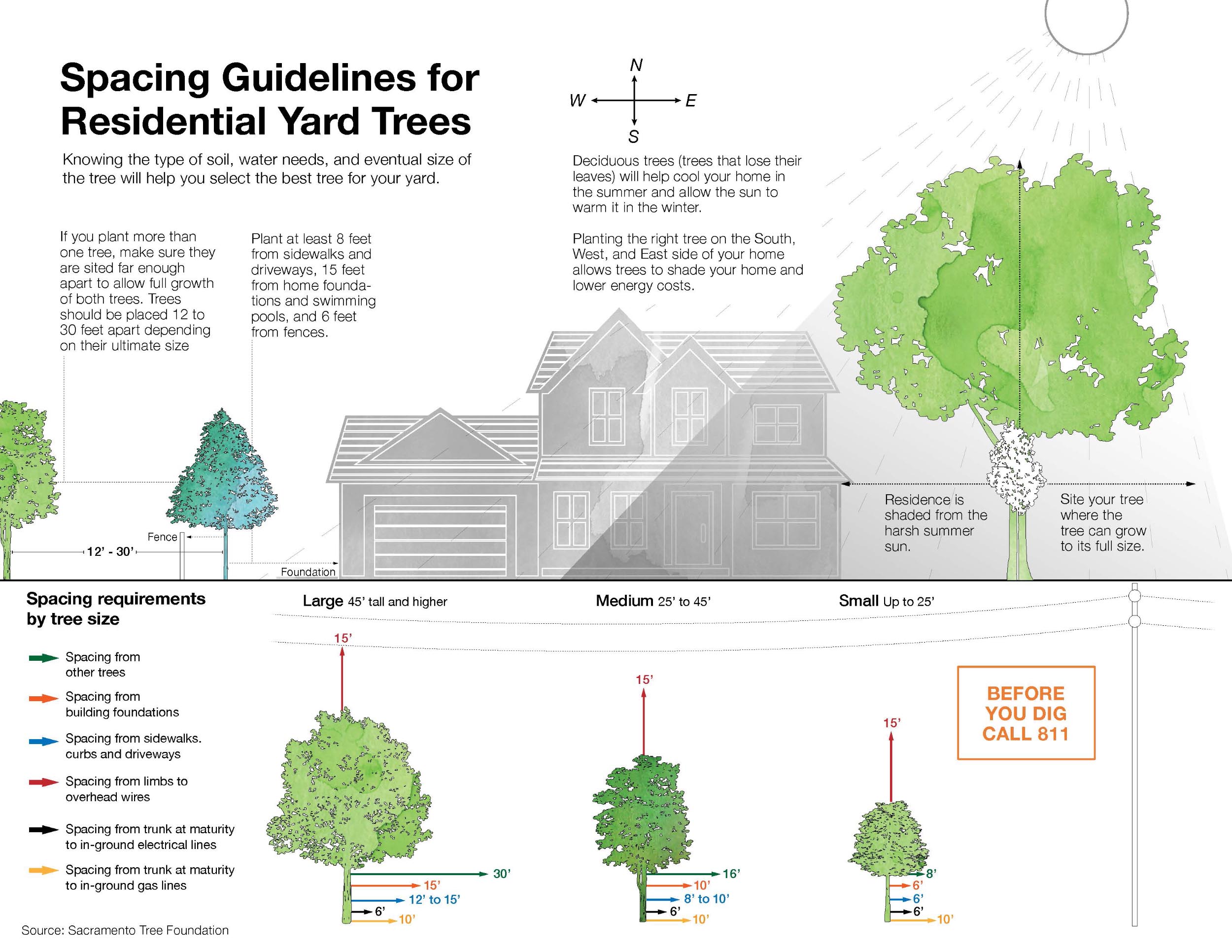
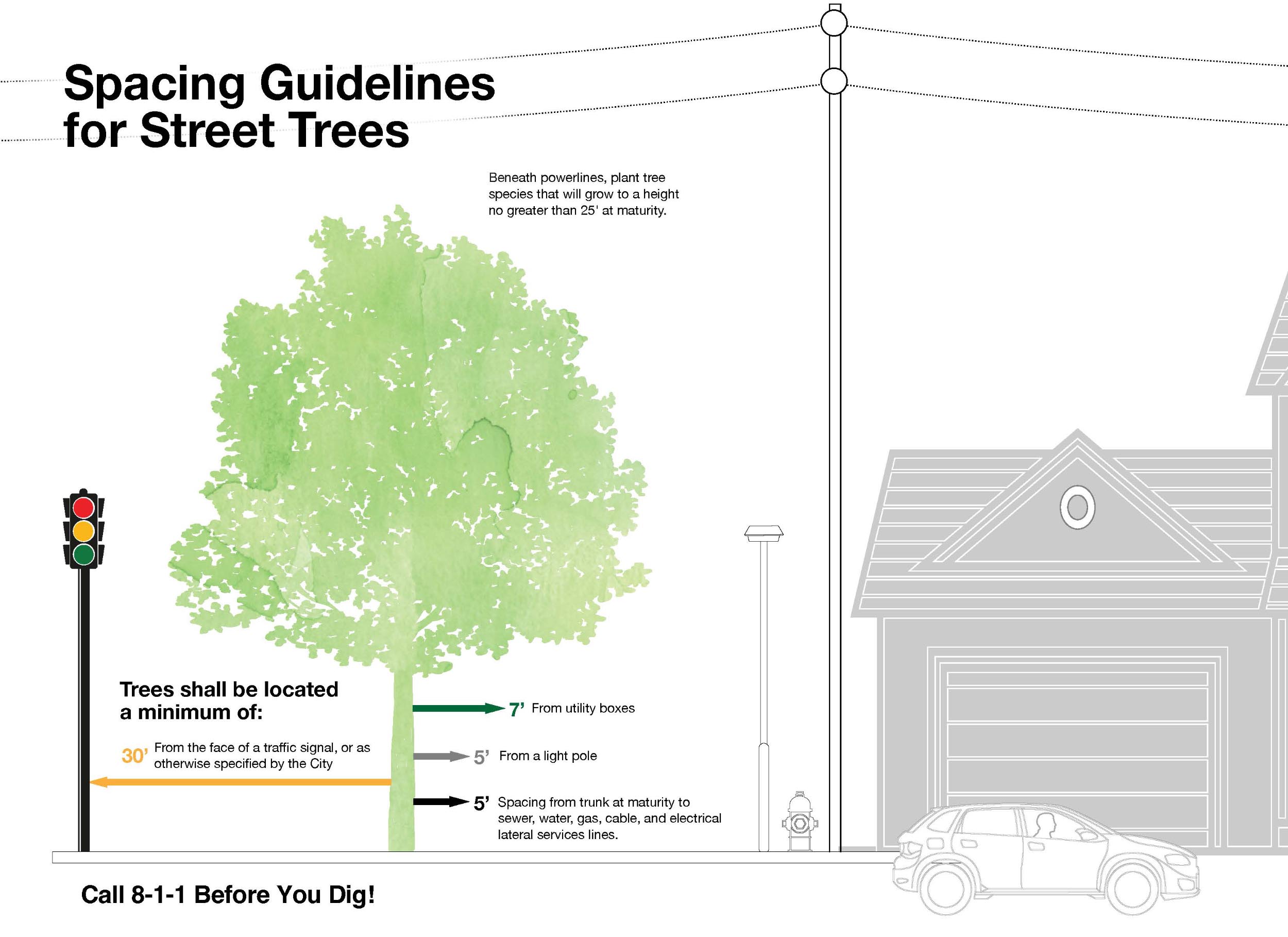
Tree Spacing Guidelines
Proper tree placement in residential yards is crucial for ensuring healthy growth, preventing damage to structures, and enhancing the overall aesthetics of your property. The accompanying image, “Spacing Guidelines for Residential Yard Trees,” provides essential information on how to determine the ideal location for planting different types of trees based on their ultimate size. By considering factors such as soil type, water needs, and proximity to buildings, sidewalks, and fences, homeowners can create a harmonious and sustainable landscape. This guide also highlights the benefits of strategic tree placement, such as energy savings and improved comfort within the home, and emphasizes the importance of adhering to recommended spacing requirements to allow trees to thrive without interference.
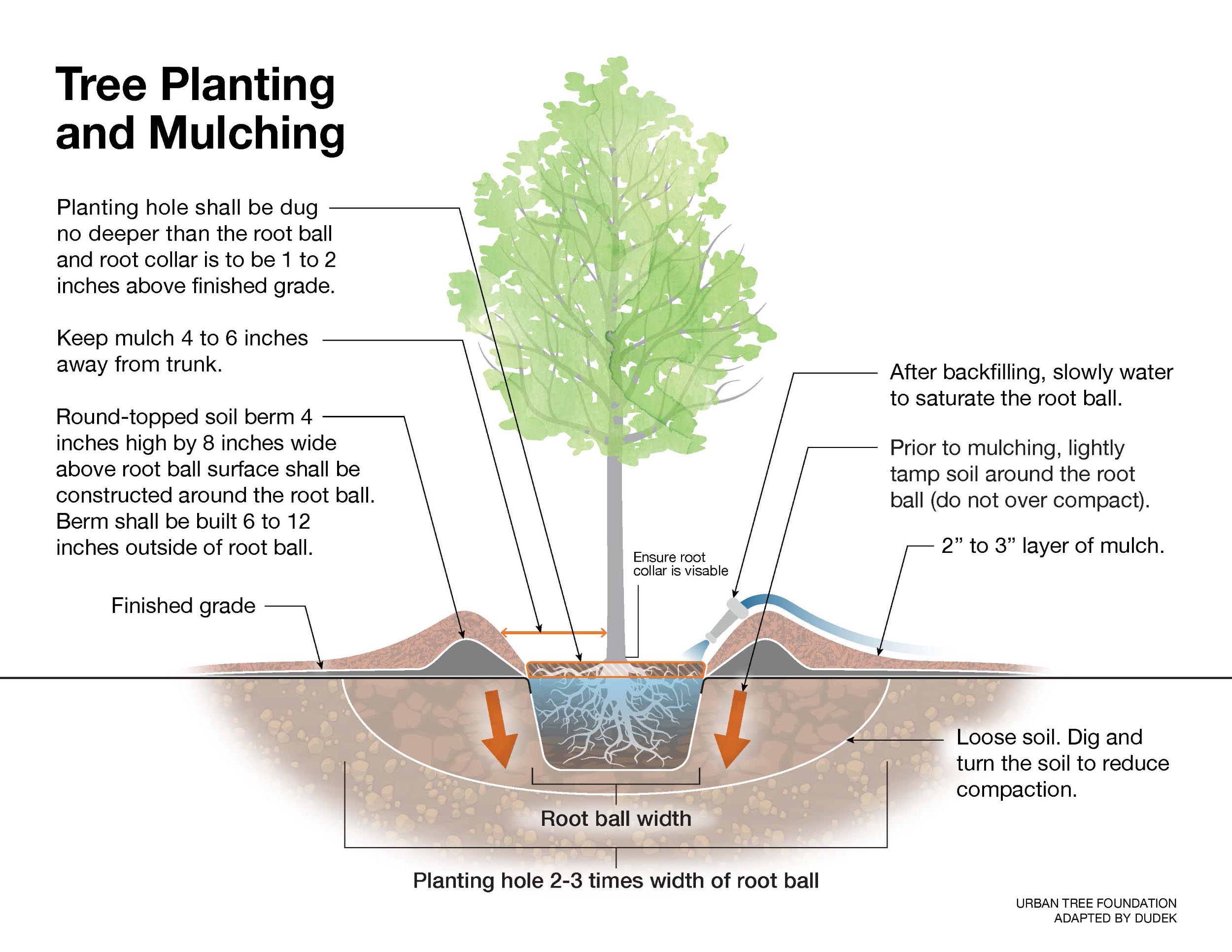
Tree Planting and Establishment Care
Proper tree planting and mulching techniques are essential for ensuring the health and longevity of newly planted trees. The following guidelines provide detailed instructions on how to correctly plant a tree, apply mulch, and maintain the tree during its establishment phase. By following these best practices, you can promote healthy root development, reduce competition from weeds, and protect the tree from environmental stresses.
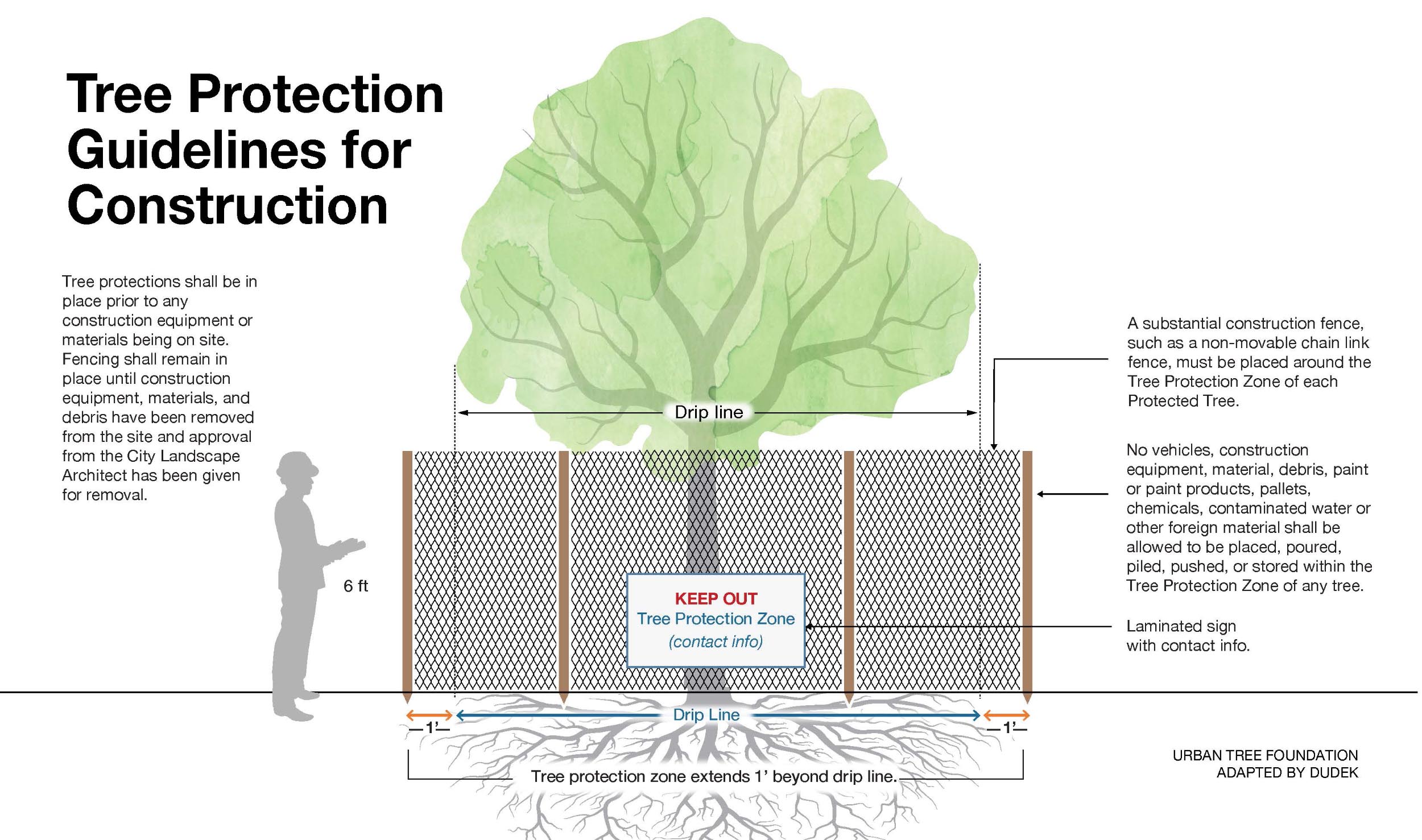
Tree Protection Guidelines
During construction projects, it’s essential to protect existing trees to ensure their health and longevity. The following guidelines illustrate the necessary steps and precautions for establishing a Tree Protection Zone around construction sites. By adhering to these practices, you can prevent damage to tree roots, trunks, and canopies, and ensure that trees remain an integral part of the landscape after the construction is completed.